Electrical Cables & Wires Guide | Low, Medium, High Voltage, Fiber Optics & More
Introduction to Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical cables and wires are the lifelines of modern infrastructure, powering everything from homes to industries. Understanding the different types—low voltage, medium voltage, high voltage, overhead lines, fiber optics, and more—is essential for safe and efficient electrical systems. This guide breaks down their features, applications, and benefits to help you make informed decisions.
1. Low Voltage Cables
- Voltage Range: Up to 1 kV.
- Applications:
- Residential wiring (lights, outlets).
- Small appliances and electronics.
- Common Types:
- THHN/THWN: Thermoplastic insulation for indoor use.
- Romex (NM-B): Non-metallic sheathed cables for homes.
- Benefits: Cost-effective, easy to install.
Keywords: low voltage cables, THHN wire uses
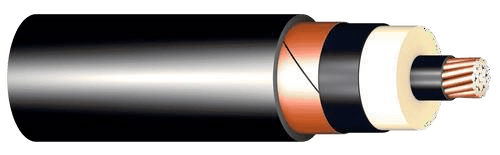
2. Medium Voltage Cables
- Voltage Range: 1 kV to 35 kV.
- Applications:
- Industrial machinery.
- Commercial buildings and power distribution.
- Insulation Types:
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): High thermal resistance.
- EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber): Flexible and durable.
- Benefits: Reliable performance under moderate stress.
Keywords: medium voltage cables, XLPE insulation
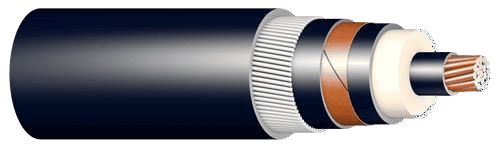
3. High Voltage Cables
- Voltage Range: Above 35 kV.
- Applications:
- Power transmission over long distances.
- Substations and grid connections.
- Features:
- Shielding: Prevents electromagnetic interference.
- Oil-Filled Cables: For extra insulation in extreme conditions.
- Benefits: Efficient energy transfer with minimal losses.
Keywords: high voltage cables, power transmission cables
4. Overhead Lines (OHL)
- Function: Transmit power over long distances via poles and towers.
- Materials:
- AAC (All Aluminum Conductor): Lightweight, corrosion-resistant.
- ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced): High strength for long spans.
- Applications:
- Rural electrification.
- High-voltage transmission networks.
- Benefits: Cost-effective for large-scale projects.
Keywords: overhead power lines, ACSR cables
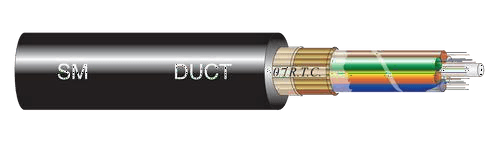
5. Fiber Optic & Telephone Cables
- Function: Transmit data via light signals.
- Types:
- Single-Mode Fiber: Long-distance communication (e.g., internet backbones).
- Multi-Mode Fiber: Short-distance (e.g., LANs, data centers).
- Applications:
- Telecommunications, broadband networks.
- CCTV and security systems.
- Benefits: High bandwidth, immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Keywords: fiber optic cables, telephone cable uses
6. Aluminum & Copper Rod Plant
- Function: Produce raw materials for cable manufacturing.
- Materials:
- Copper Rods: High conductivity for electrical wires.
- Aluminum Rods: Lightweight and cost-effective for OHL.
- Applications:
- Wire drawing and cable production.
- Electrical components and connectors.
- Benefits: Ensures quality and consistency in cable manufacturing.
Keywords: copper rod plant, aluminum rod uses
7. XLPE & PVC Insulation
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene):
- Properties: High thermal and chemical resistance.
- Applications: Medium/high voltage cables, underground installations.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride):
- Properties: Flexible, flame-retardant.
- Applications: Low voltage cables, household wiring.
- Benefits: Enhances durability and safety.
Keywords: XLPE vs PVC, cable insulation types
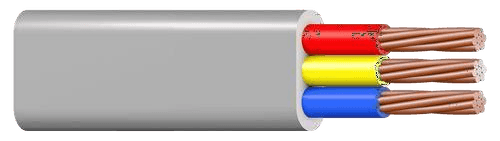
8. Wires
- Types:
- Solid Wires: Single conductor for stable connections.
- Stranded Wires: Multiple thin strands for flexibility.
- Applications:
- Circuit boards, automotive wiring.
- Home appliances and electronics.
- Benefits: Versatile and easy to install.
Keywords: stranded vs solid wires, electrical wire uses
Comparison Table: Electrical Cables & Wires
| Type | Voltage Range | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage Cables | Up to 1 kV | Residential wiring, appliances |
| Medium Voltage Cables | 1 kV–35 kV | Industrial, commercial power |
| High Voltage Cables | Above 35 kV | Long-distance power transmission |
| Fiber Optic Cables | N/A | Data transmission, telecom |
| Overhead Lines (OHL) | N/A | Rural electrification, grids |
How to Choose the Right Cables & Wires
- Voltage Requirements: Match cable ratings to your system’s voltage.
- Environment: Use XLPE for underground or high-heat areas.
- Flexibility: Stranded wires for tight spaces; solid wires for stability.
- Compliance: Ensure adherence to NEC, IEC, or local standards.
Benefits of Quality Electrical Cables
- Safety: Prevents short circuits and fires.
- Efficiency: Reduces energy losses during transmission.
- Durability: Withstands harsh conditions for years.
FAQ Section
Q: What’s the difference between XLPE and PVC insulation?
A: XLPE offers higher thermal resistance, while PVC is more flexible and cost-effective.
Q: Can I use low voltage cables for industrial applications?
A: No—industrial setups typically require medium or high voltage cables.
Q: Are fiber optic cables better than copper?
A: For data transmission, yes—fiber optics offer higher speeds and bandwidth.
Q: What’s the lifespan of overhead power lines?
A: 30–50 years, depending on material and maintenance.
Conclusion
From low voltage household wiring to high voltage transmission lines and fiber optic data cables, choosing the right electrical cables and wires ensures safety, efficiency, and reliability. Prioritize quality materials and compliance with industry standards for optimal performance.
Upgrade your electrical systems today with the right cables and wires—powering progress with precision!